Restorative Dental Care for Children in Puget Sound
Restorative Care
Pediatric restorative dentistry encompasses the diagnosis and treatment of damaged, decayed, or developmentally abnormal teeth in children. At Puget Sound Pediatric Dentistry, our restorative care program is designed to repair compromised teeth, restore proper function, maintain space for permanent teeth, and preserve the aesthetics of your child’s smile—all while ensuring their comfort and psychological well-being throughout the process.
Restorative Care
Protect Your Child's Smile
While prevention is key, restorative treatments are sometimes necessary when cavities occur. The CDC reports that about 45% of children ages 2–19 have had cavities, making timely care vital for stopping decay, relieving pain, and supporting healthy development.
Space Maintainers
Appliances to preserve space following the premature loss of primary teeth.
Tooth Extraction
Gentle removal of severely damaged or infected teeth when restoration isn’t possible.
The Philosophy of Pediatric Restorative Care
How We Treat Every Case With Care
Our restorative philosophy centers on conservative, child-focused treatment that addresses both the immediate dental problem and its underlying causes. We believe in preserving as much natural tooth structure as possible while providing durable, functional restorations that will serve your child well throughout their developmental years.
Key Tenets of Our Restorative Approach:
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Using the least invasive effective treatment to preserve natural tooth structure.
- Early Intervention: Addressing problems promptly to prevent more extensive damage
or spread of infection. - Family-Centered Care: Involving parents in decision-making and home care
education.

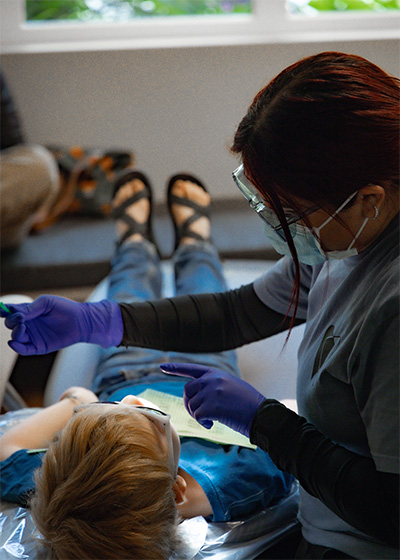
Tooth-Colored Composite Fillings
Safe, Strong, and Natural-Looking
Tooth-colored composite fillings have become the standard of care for most pediatric restorations, offering excellent aesthetics, conservative preparation requirements, and direct bonding to tooth structure.
Composite Filling Materials
Material Composition:
- Resin matrix: Organic polymer that provides the base structure
- Inorganic fillers: Glass or ceramic particles that enhance strength and wear resistance
- Coupling agents: Chemicals that bond the resin and filler components
- Initiators and accelerators: Compounds that trigger and control the setting reaction
- Pigments and opacifiers: Additives that create a natural tooth-like appearance
Types of Composites:
- Nanofilled composites: Containing extremely small particles for superior polish and strength
- Hybrid composites: Combining different particle sizes for optimal properties
- Flowable composites: Lower viscosity materials for specific applications
- Bulk-fill composites: Materials designed for placement in thicker layers
- Glass ionomer-composite hybrids: Combining fluoride release with composite
durability
Space Maintainers
Space Maintenance Following Early Tooth Loss
Space maintenance is a critical component of pediatric restorative dentistry, addressing the consequences of premature primary tooth loss to prevent orthodontic complications and ensure proper permanent tooth eruption.
The Importance of Space Maintenance
Consequences of Premature Tooth Loss:
- Space loss: Adjacent teeth drift into the space left by the lost tooth
- Eruption pathway obstruction: Permanent teeth may be blocked from proper
eruption - Crowding: Insufficient space for permanent teeth to emerge properly
- Impaction: Permanent teeth may become trapped beneath the gum line
- Midline shifts: Dental midlines may become misaligned
- Bite problems: Changes in occlusion can develop
- Increased orthodontic complexity: More extensive and costly treatment may be needed later
Benefits of Space Maintenance:
- Preserves arch length: Maintains the proper dimensions of the dental arch
- Guides eruption: Helps permanent teeth emerge in their proper positions
- Prevents tipping: Keeps adjacent teeth from tilting into the space
- Reduces orthodontic needs: May minimize or simplify future orthodontic treatment
- Maintains function: Preserves chewing ability and speech development
- Cost-effective: Less expensive than correcting problems later
- Developmental support: Facilitates normal jaw and facial development
Tooth Extraction
Gentle Tooth Extractions for Kids
Pediatric extractions and oral surgery procedures are sometimes necessary components of comprehensive restorative care when teeth cannot be saved or when other surgical interventions are required for optimal oral health.
Indications for Pediatric Extractions
Primary Tooth Extraction Indications:
- Severe decay: Teeth with extensive caries not amenable to restoration
- Pulpal infection: Abscessed teeth with non-restorable pulpal involvement
- Mobility: Significantly mobile teeth near natural exfoliation
- Orthodontic considerations: Removal to alleviate crowding or facilitate treatment
- Over-retained teeth: Primary teeth preventing normal eruption of permanent successors
- Trauma: Severely fractured or luxated teeth with poor prognosis
- Developmental anomalies: Supernumerary or malformed teeth
Permanent Tooth Extraction Indications:
- Severe decay: Extensively damaged teeth beyond restoration
- Advanced periodontal disease: Teeth with poor supporting structures
- Orthodontic planning: Strategic removal to address crowding or malocclusion
- Impacted teeth: Teeth unable to erupt into proper position
- Supernumerary teeth: Extra teeth interfering with normal development
- Severe trauma: Teeth with poor prognosis following injury
- Infection control: Removal of source of persistent infection
Frequently Asked Questions About Restorative Care
What Every Parent Should Know
Is it really necessary to fix cavities in baby teeth?
Yes, absolutely. Untreated cavities in baby teeth can lead to pain, infection (abscess), difficulty eating, and damage to the developing permanent teeth underneath. Baby teeth are also crucial for holding space for permanent teeth, and their premature loss can cause significant orthodontic problems.
What is the difference between a filling and a crown?
A filling is used to repair a smaller area of decay within a tooth. A crown is a full-coverage restoration that covers the entire tooth. Crowns are used when the decay is too extensive for a filling, after pulp therapy (nerve treatment), or for teeth with developmental defects, as they provide superior strength and protection.
Will my child need to be put to sleep for restorative treatment?
Not necessarily. The need for sedation depends on your child’s age, anxiety level, ability to cooperate, and the extent of the planned treatment. Many children do well with just local anesthesia and our expert behavior guidance techniques. For more anxious or younger children, or extensive treatment, we offer options like nitrous oxide (“laughing gas”), oral sedation, or general anesthesia to ensure their safety and comfort.
My child’s permanent front tooth is chipped. Can it be fixed?
Yes. In most cases, chipped permanent teeth can be beautifully repaired using tooth-colored composite bonding material. If you have the broken fragment, bring it with you, as it can sometimes be reattached. It is important to have any dental trauma evaluated promptly.
Let's Get Started
Start Your Child's
Journey Today!
The foundation for a lifetime of healthy smiles begins in childhood. By establishing good dental habits early and maintaining regular preventive care, you’re giving your child the gift of excellent oral health. Our team is ready to partner with you on this important journey. Schedule your child’s first visit today and see why families throughout Washington trust Puget Sound Pediatric Dentistry with their children’s dental care.

